Neurology private practice In Budapest
Over 18 years only
Specialist neurology clinic
Neurology is a medical discipline dealing with the structural and functional diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system. At the Buda Musculoskeletal Private Clinic - uniquely in Hungary - we provide outpatient rehabilitation for patients who have suffered a stroke.
The special feature of this method is that we develop several skills at the same time, in addition to motor skills, speech, writing, reading, memory and psyche, and achieve better results by supporting them together. After a neurological assessment, we run 8-week courses with the help of a speech therapist, neuropsychologist, physiotherapist and occupational therapist. For more information, please contact our reception.
During the examination, an outpatient form is completed for each patient.

How do we get a diagnosis?
- Often, a history and a thorough physical examination are sufficient, but in some cases imaging diagnostics or even laboratory tests are needed.
- We organise the tests recommended by the specialist (laboratory, X-ray, ultrasound, CT, MR) for our patients and ensure that the necessary tests are carried out within 24-72 hours at our partner institutions, where the best diagnostic equipment and specialists are waiting for our patients.
- We receive the artefacts in electronic format.
What methods do we use to treat?
- prescription: prescription of medicines, medical devices
- physiotherapy: physiotherapy, manual therapy, massage
- physiotherapy: ultrasound, electrotherapy, bioptron treatment, shockwave treatment
- surgeries: neurosurgery consultation if indicated, organisation of operations in our partner institutions in hospital in-patient wards if necessary, on the advice of the examining specialist
Further neurological tests
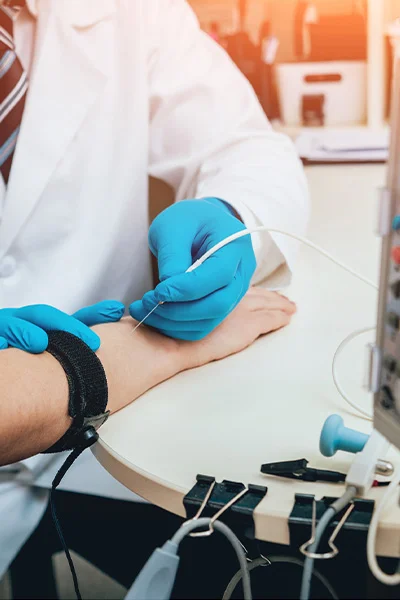
From ENG (electroneurographic) examination provides information about the condition and function of the nerves in the area. The test involves stimulating the nerves with an electric current and recording the response detected by an electrode placed on the muscle supplied by the nerve. The test is suitable for the detection of diseases of individual surrounding nerves (mononeuropathies), such as tunnel syndromes (e.g. carpal tunnel syndrome) and generalised diseases of the surrounding nervous system (polyneuropathies). It is also suitable for the detection of diseases of the nerve-muscle transition (myasthenia gravis). It is also useful to distinguish between damage to nerve roots (radiculopathy) and nerve plexus involvement, and can confirm diseases of the spinal motor neurons.
From EMG (electromyography) test to get information about how the muscles are working. During the test, a thin needle electrode is inserted into the muscle and the electrical response is recorded at rest or during muscle movement or tensing. The test often gives information when evaluated in conjunction with the ENG test. It is an essential procedure in the case of muscle diseases and pathologies associated with muscle inflammation, but it can also be used to assess the degree of nerve regeneration and to distinguish between acute and chronic diseases (e.g. polyneuropathy).
The electroneurography (ENG) and electromyography (EMG) tests Dr. Magdolna Simó clinical neurophysiologist assistant professor and Dr. Beatrix Vághy by a neurologist In our private practice in Pest (XIII district).
What happens during the neurological examination?
By providing short appointment times, the following diseases can be identified and treated, the necessary follow-up examinations coordinated, and the patient's long-term professional care provided, even in collaboration with the general practitioner:
- Stroke (brain diseases, stroke, stroke), assessing stroke risk, organising additional tests, care of stroke patients according to risk factors, planning of follow-ups, organisation of additional tests, regular monitoring, appropriate medication specific to the cause of the disease, lifestyle advice.
- multiple sclerosis: diagnosis, differential diagnosis, indication of treatment according to the aetiology, organisation of treatment, regular monitoring, lifestyle advice.
- Dizziness: dizziness is usually caused by an abnormal functioning of the inner ear's balance organ, which senses the movement of the head. In most cases, vertigo is accompanied by an abnormal, rhythmic eye movement. The primary aim is to identify the cause of the vertigo. In our neurology practice, we make an initial diagnosis and, after carrying out diagnostic tests, we make a therapeutic recommendation.
- Walking disorder, differential diagnosis of neuropathies, Parkinson's disease, various over-movements, paralysis, diagnosis of the cause of forgetfulness, back and neck pain.
- Headaches: the cause of the headache should be investigated by a neurologist. A detailed investigation of the circumstances, the onset and course of the complaints, and an evaluation of the symptoms are carried out. It is the identification of the cause that sets the therapeutic goal. Headache can be tensiogenic, when stiffness of the neck and neck muscles triggers the pain. Treatment in this case consists of physiotherapy, relaxation exercises and physical therapy. It may be migraine or other organ cause. Laboratory tests, CT scan of the skull, MRI, EMG scans may be necessary.
Our patients' opinions
Our neurologists

Dr. László Csiba PhD
PhD D.Sc. academic, university professor

Dr. Beatrix Vághy
Neurologist and neurophysiologist

Dr. Magdolna Simó PhD
Associate Professor, neurologist, clinical neurophysiologist

Dr. Sándor Horváth PhD
Neurologist, candidate of medicine, associate professor