Knee pain: causes, treatment options and the role of axis correction
What can cause knee pain?
A knee pain one of the most common musculoskeletal complaint, which can affect anyone, regardless of age. The cause of pain can be acute injury, overuse, or chronic lesions, for example, cartilage damage. In younger people, knee injuries, ligament sprains and cartilage injuries from sports are predominant, while in older people, abrasions such as osteoarthritis are the main cause.
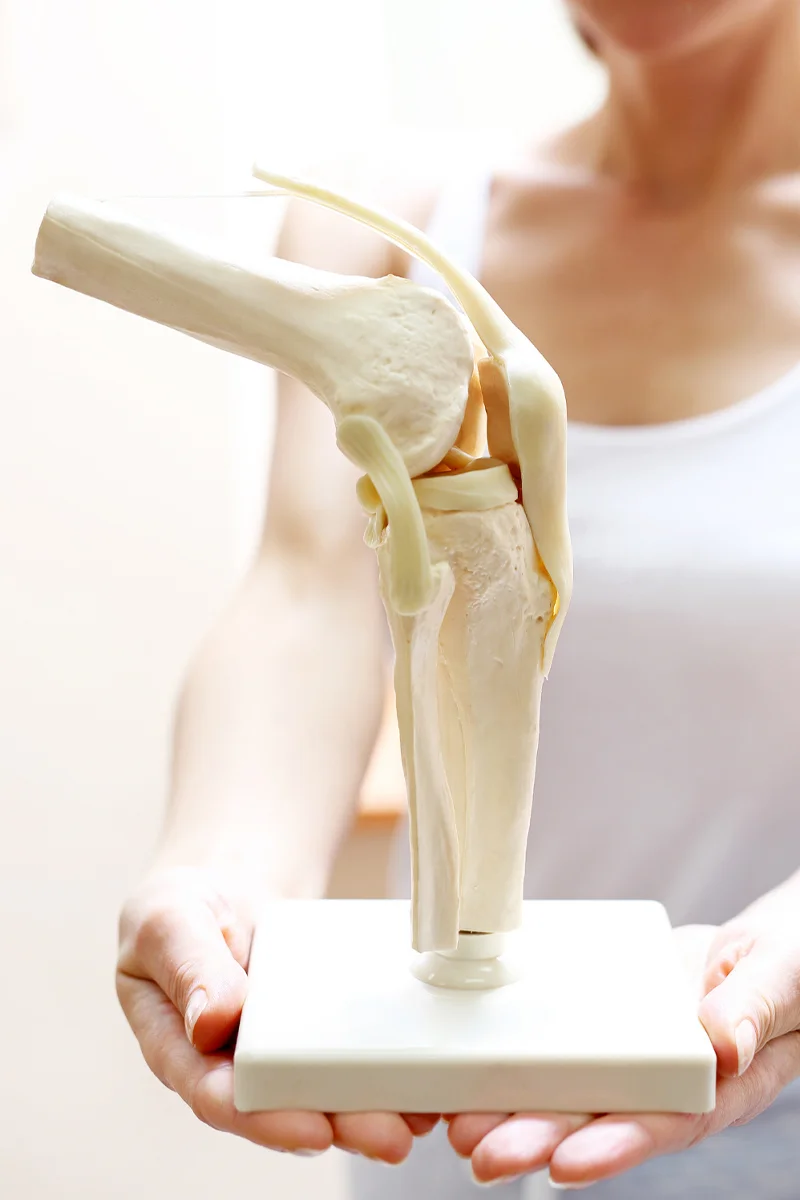
Anatomy of the knee in a nutshell
The knee joint is a complex, hinge-like joint located at the junction of the femur, tibia and patella. Stability is provided by ligaments and muscles, and friction is reduced by cartilage surfaces during movement. Any of its elements injury or wear and tear can cause knee pain.
Most common causes of knee pain in young and old people
- Sports injuries (e.g. torn ligaments, cartilage tears)
- Overloading, incorrect loading
- Uneven load due to misalignment
- Osteoarthritis, cartilage wear
- Inflammatory diseases (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis)
When is knee pain „normal” and when should you see a doctor?
Occasional mild pain after sport or hiking may be normal, but if the pain is recurrent, it increases with movement, swelling or instability, an examination by an orthopaedic specialist is essential.
Unstable knee - when the knee „slips” out of place
What is unstable knee?
An unstable knee is a condition where the knee joint is unable to maintain its stability in motion. The knee often feels "slippery" and unstable, especially when stepping on stairs or changing direction suddenly, but also when walking on flat ground.
Causes of unstable knee - injury, ligament tear, misalignment
Instability may be caused by previous knee injuries, such as anterior cruciate ligament tears or lateral ligament strains. But common triggers the shaft misalignment which puts excessive long-term stress on one side of the joint.
Association between unstable knees and knee pain
The lack of stability exposes the knee joint to constant micro-injuries, which over time can lead to knee pain, cartilage wear and inflammation.

Dr. Péter Doszkocs
Orthopaedic traumatologist, hip and knee surgeon, lower limb specialist, robotic surgeon
Online booking:
Budafoki Road surgery: Thursday
Bokor street surgery: Week of the other days
Please choose the service that suits you
Control fee: 25 000 HUF, for 3 months after the initial examination, for the same complaint.
- 1. Select the service you need from the drop-down box!
- 2. Use the calendar to choose a date that suits you!
- 3. Enter your details to register or login with your previous registration!
- 4. If you would like to make a reservation on behalf of someone else (e.g. your child), please let us know at the location provided.
- 5. Briefly describe your complaints!
- 6. Select the type of consultation: initial examination, control examination or prescription.
- 7. Click on the button to book your appointment. Thank you for choosing BMM!
If you are unable to make the appointment you have already booked, please, at least 24 hours before notify us of your intention to withdraw. This gives other patients the opportunity to get the medical care they need in time. Thank you for your cooperation and understanding!
Resignation: +36 1 44 33 433
If for the week of your choice cannot find an available appointment, for further assistance, please call our call-center at +36 1 44 33 433-phone number! Our staff will be happy to help you make an appointment with the doctor of your choice or another specialist according to your complaint.
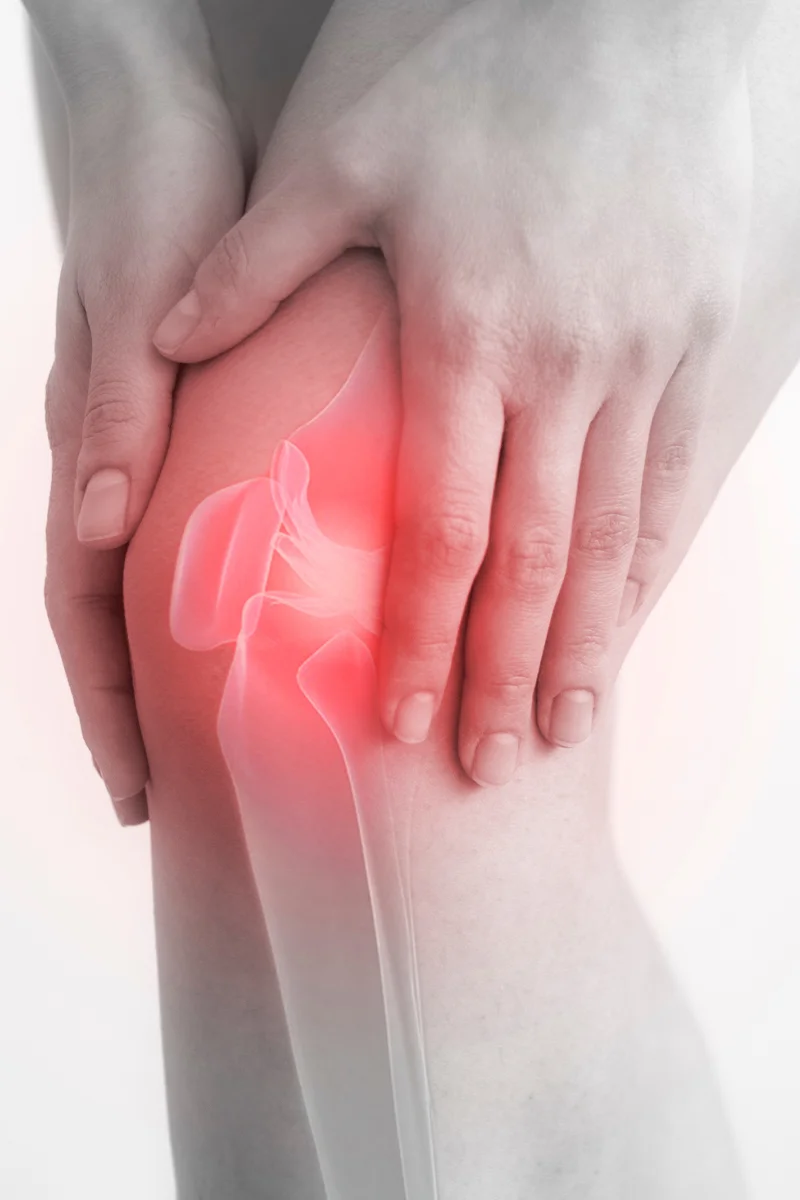
Knee axis correction: treating the hidden cause
What is shaft misalignment and how does it cause knee pain?
Axial misalignment means that the leg and the femur does not form a straight axis, i.e. the knee takes the shape of an "X" or "O". This biomechanical asymmetry overloads one side of the joint, which can lead to long-term pain and cartilage wear.
How does knee axis correction help relieve pain?
The aim of the axis correction is to evenly distribute the load on the knee joint. The procedure involves surgically reshaping the bone to straighten the static line of the foot. This significantly reduces pressure in overloaded areas, thus reducing pain and slowing wear.
How does knee axis correction help relieve pain?
The aim of the axis correction is to evenly distribute the load on the knee joint. The procedure involves surgically reshaping the bone to straighten the static line of the foot. This significantly reduces pressure in overloaded areas, thus reducing pain and slowing wear.
Conservative treatment vs. surgical solution
For minor shaft misalignments physiotherapy, insoles and muscle strengthening can also help. In more severe cases, however, knee surgery with axis correction is the only effective solution.
When is axle correction surgery recommended?
Step-by-step procedure of the surgery
- Preparations and planning:
Before the procedure, detailed imaging tests (e.g. X-rays, MR) are used to determine the degree of axial misalignment and the exact direction of correction. - Creating access:
The surgeon will dissect the corresponding part of the tibia or femur where the axis correction will be made. - Partial cutting of the bone (osteotomy):
Under X-ray control, the bone is precisely cut at a predetermined angle so that the bone fragments can be moved into the new position. So there is no complete resection. - Setting the correction:
The bone pieces are adjusted to the ideal axial position to avoid unilateral loading on the knee. - Fixing:
The adjusted bone ends are fixed with special titanium plates and screws to ensure that the bone heals stably and safely. - Closure and rehabilitation preparations:
The wound is closed and then healing and physiotherapy can begin, which is key to a full recovery of function.
Recovery time, rehabilitation and return to exercise
After surgery, you will usually 6-8 weeks recovery time to be counted, followed by the physiotherapy, which helps to regain range of motion and muscle strength in the joint. For a full recovery up to 3-6 months may be necessary.
What results can the patient expect?
Successful axle correction surgery can significantly reduce pain, improves knee stability and can help avoid or delay the need for knee replacement.
Treating knee pain: movement therapy, lifestyle changes, surgery
Physiotherapy and muscle strengthening
The primary treatment for musculoskeletal complaints is physiotherapy. It can be used to strengthen muscles, increase range of motion and relieve joint stress through a targeted series of exercises.
Load reduction and lifestyle changes
Excess weight, poor posture or lack of exercise can also worsen the condition of the knee. Lifestyle changes such as weight loss or wearing the right shoes, can lead to serious improvements.
When is surgery unavoidable?
If the knee pain becomes persistent, conservative treatment does not improve, or the degree of axis misalignment is large, knee axis correction surgery may be necessary.

Dr. Péter Doszkocs
Orthopaedic traumatologist, hip and knee surgeon, lower limb specialist, robotic surgeon
Please contact Dr. Péter Doszkocs - the knee specialist
If your knee pain is caused by instability or a misalignment, don't delay! Dr. Doszkocs Péter Orthopedic-traumatologist senior physician specialises in the treatment of knee joint problems, with a particular focus on axis correction surgery.
As a highly skilled and precise specialist, she creates a personalised treatment plan for her patients, whether it is conservative therapy or surgical solutions.
Take the first step towards pain-free movement - make an appointment with Dr. Peter Doszkocs!
