Backbone hernia

Dr. Bence Moravcsik
Orthopaedic traumatologist
What is a herniated disc?
The spinal hernia the formation of a spinal column in a given part of the spinal column degenerative - i.e. wear - lesion. Most often in the spine Lumbar, as well as in the neck, can be accompanied by sharp pain and even numbness or restricted movement.
The spinal column vertebrae between which the flexible connection is made by the so-called. cartilages ensure. The discs consist of two parts: consisting of an outer circular fibrous ring and an inner jelly-like core. The intervertebral discs are the “shock absorbers” of our spine, ensuring the mobility and flexibility of the spinal column.
In a herniated disc, the outer fibrous ring of the disc ruptures and the nucleus pulposus protrudes through it. This is called disc prolapse. Because of the protrusion the nerve roots exiting the spinal cord may come under pressure, they can become pinched and inflamed, and even damaged. Damage to the nerve fibres can lead to long-term disability and even paralysis. A herniated disc can rupture if not properly treated and attended to and can cause severe pain and movement restriction, generating further nerve damage.
What is the difference between herniated disc and herniated disc?
A herniated disc is also known as a herniated disc. There is no difference in meaning between the two terms.
How is it formed?
The development of a herniated disc is rarely linked to injury or trauma. In most cases, it comes slowly, gradually, over years this degeneration. The fibrous rings of the discs are elastic due to their high water content. However, the water content of the discs steadily decreases after the age of 20-25 years, so the discs become dehydrated and start to wear. As the water content of the disc decreases, the gelatinous inner part behind the fibrous outer part of the disc protrudes, which can put pressure on or damage the nerve root exiting the spinal cord.
The slow wear and tear process is also greatly influenced by various lifestyle factors, as well as sudden injuries and traumas. Office workers, people with sedentary lifestyles, people who do heavy physical work and athletes are also particularly at risk. Scoliosis and other spinal diseases are an additional predisposing risk.
Diagnosis of spinal hernia
The diagnosis is made by an orthopaedic specialist or rheumatologist sets up. We have developed a specific patient journey protocol at BMM out to ensure thorough investigation and effective, targeted therapies.
Our mission is to help our patients regain their freedom of movement as soon as possible, and to permanently and long term relief from painful complaints.
Building blocks for a successful investigation based on the BMM patient journey protocol:
- A medical history already half a diagnosis, with detailed questioning many diseases can be ruled out.
- Thorough physical examination by a specialist. Based on the physical examination, a specialist will determine the need for any diagnostic imaging tests. Diagnostic imaging tests can help to visualise and measure anatomical structural changes, and reveal the true cause of the complaint.
- X-ray examination of the spine bony lesions can be confirmed. This is often necessary for differential diagnosis.
- The condition of the soft tissues, discs, articular cartilage, muscles and tendons is accurately assessed by the radiograph.
- In cases of disc herniation, an accurate diagnosis is often MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan is also necessary.
- In the case of nerve involvement, neurophysiological testing, ENG or EMG is recommended to determine the extent of suspected nerve damage.
Neuroconductive neurophysiological examinations (ENG/EMG) are available at BMM's clinics in Pest and Óbuda. Necessary spinal X-rays, ultrasound, CT and spinal MRI examinations are provided by our partner institutions at an off-site location for an additional fee.
- Based on the medical history, physical examination and imaging diagnostics, the orthopaedic specialist makes an accurate diagnosis.
- A personalised treatment plan is drawn up, including a specific spinal physiotherapy is.
- The care of this spinal hernia patient is not over yet. Our team of professionals (doctor, physiotherapist, physiotherapist-masseur) will continue to monitor the patient's condition, help him change his lifestyle and maintain long-term pain-free living.
- We accompany our patients all the way to recovery!
Symptoms of herniated disc
The main symptom of a herniated disc is spinal pain, which is associated with additional neurological symptoms: numbness, shooting pains, pins and needles, loss of sensation, possibly incontinence or bowel movements. Symptoms are greatly influenced by the location of the hernia.
Hernia of the lumbar spine
The most common type is herniated lumbar spine, in which case the sciatic nerve is affected. The main symptom of a lumbar hernia is isias. In such cases, severe pain in the lower back is accompanied by numbness and a sensation of pain radiating down the legs. One of the most common causes of sciatica is lumbar hernia.
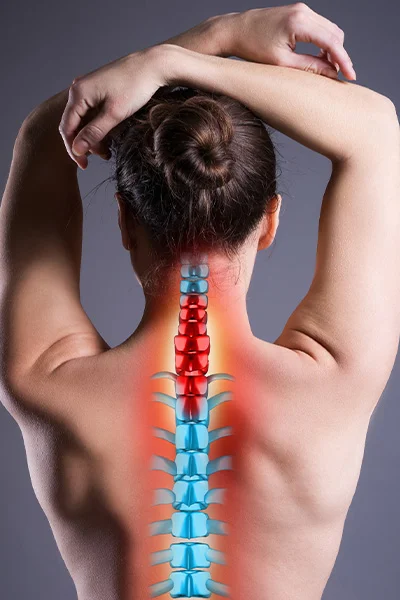
Cervical spinal hernia
A herniated cervical spine is also a common pathology. In such cases pain and numbness radiate to the shoulders and arms, but can also cause headaches, loss of balance or even tinnitus. The pain in the neck is also of the sharp, sudden type that increases with sudden movement.
Rarely, a herniated disc develops in the middle back. In this area, the ribs provide more support, so the vertebrae and discs in this area are under less strain.
If you have any of the following symptoms of a hernia affecting any part of your spine, you should see an orthopaedic, rheumatology or neurology specialist as soon as possible for an examination:
- pain radiating from the spinal cord to the limb
- limb numbness
- emotional disturbance, loss of sensation
- muscle weakness
- an ant-like or pins-and-needles feeling in the limbs
- limb paralysis (even temporary!)
- incontinence, constipation.
Typically, the pain can be triggered by body position or movement, for example, the pain is increased by coughing, sneezing, medical examination techniques.
The key to success is doctor-patient cooperation and trust!

Symptoms of herniated lumbar spine
Herniation most often occurs in the lumbar spine and is called a lumbar herniation. This is the area where the intervertebral discs are subjected to the most stress during everyday life. In sedentary work, it is the prolonged sitting itself that can cause problems, and in sports or physical work, inappropriate lifting techniques can cause problems. The lumbar spine for most people is unstable to some degree, so highly vulnerable. It only takes one wrong move or even a sustained negative strain to develop a lumbar hernia.
A herniated disc in the lumbar region usually affects the sciatic nerve, pressurising or pinching it. The sciatic nerve starts in the spinal cord and runs down the pelvic bone to the legs. In the lumbar region, it passes in close proximity to the lumbar vertebrae and discs, so it is easily damaged in the event of a hernia. A pain or numbness in the thighs or legs the main symptom of this - also known as also known as sciatica this syndrome.
Lumbar herniated disc needs professional treatment as soon as possible - even if the pain and other symptoms are not persistent or do not significantly impair mobility and quality of life. A small herniated disc is also a problem that needs to be treated! With spinal physiotherapy and regular personalised exercises, lumbar disc herniation can be treated and even reversed.
Treatment of herniated discs
The treatment of a herniated disc depends on the extent and location of the hernia and the quality of the symptoms caused. In each case, a specialist will decide on the appropriate therapy after a thorough examination.
Herniated disc in most cases conservative therapy well manageable. Conservative treatment an orthopaedic, neurologist or rheumatologist is led by. Acute pain relief and inflammation reduction usually done with medication, this can be topical by injection, oral or patch; steroid or non-steroidal. Spinal decompression is also essential in the acute phase, but long-term strict bed rest is not recommended. Nerve mobilisation is recommended to release the pressurised nerve. Once the acute pain has subsided long-term conservative therapy needed. For this main element of physiotherapy, which needs to be tailored to the individual. McKenzie spinal exercises, nerve mobilisation training, manual therapy herniated discs are highly treatable, even achieving complete freedom from symptoms. In addition to physiotherapy, it is recommended to complementary physiotherapy treatments (ultrasound, TENS safe laser), medical massage, and balneotherapy treatments.
In severe cases, for a ruptured disc herniation surgical intervention justified. To assess this neurosurgery consultation and examination required. Spinal hernia surgery is performed by a neurosurgeon. Post-operative rehabilitation and further lifestyle is also a priority for the for physiotherapy van.
How can surgery be avoided?
Surgical intervention for herniated discs can most likely be avoided by regular, professional physical exercise. By performing individual, tailored and targeted exercises, the deep muscles of the spine are strengthened, reducing the load on the discs. Spinal physiotherapy should be complemented by medical massage, physiotherapy (ultrasound, TENS, safe laser treatment), possibly with balneotherapy. In addition to therapy, lifestyle also plays a big role in avoiding surgery. In the case of overweight, weight loss is recommended, as well as avoiding smoking and alcohol, following a healthy diet and drinking plenty of fluids.
The indication for surgery is always neurosurgeon specialist decide.

Causes of disc herniation
The development of disc herniation can be caused by several different factors. It is important to recognise the early signs and start treatment in time. If the symptoms persist, it is worth taking them seriously and seeing a specialist rheumatologist or spine specialist as soon as possible.
Spinal hernia is most often caused by a degenerative process, but there are factors that can increase the risk of developing a herniated disc:
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Sedentary work, incorrect sitting, poor posture
- Heavy physical work, poor lifting technique
- Serious sports activity without strengthening the deep back muscles
- Scoliosis
- Bekhterev's disease
- Other spinal diseases
The importance of prevention
The development of herniated discs can often be prevented by lifestyle changes. For known spinal conditions, it is highly recommended to visit a physiotherapist and targeted exercises to learn the to strengthen deep back muscles. In addition, the correct posture, sitting position and lifting technique learning and daily use is recommended.
The regular back massage also has a beneficial effect on the condition of the back muscles, thus reducing the strain on the spine.
A healthy lifestyle, adequate fluid intake and a diet rich in vitamins and minerals maintain healthy bones, discs, joints and muscles for a long time. Recommended minerals and vitamins.
In addition, it is recommended to regular exercise, sports such as swimming, running, walking.

Common complaints treated by specialists at the Spine Centre
- back pain
- back pain
- scoliosis
- nerve pinching
- back pain
- neck pain
- stiff neck - neck stiffness
- osteoporosis
- back pain
- spinal stenosis
- back pain
- pain in the lumbar spine
- pain in the buttocks
- neglect
- sacral pain
- shoulder blade pain
- morning backache
- pain in the back of the neck
